EV Battery Voltage & Battery Capacity
- In this article, two wheelers, three wheelers and four wheelers battery voltage and battery capacity, types of EV Charger and methods of charging is given.
- The details of electrical vehicle battery voltage, battery capacity for two-wheel, three wheel and four wheel is given below.
|
Types of vehicles |
Battery voltage |
Battery capacity ( kwh
) |
|
E – Two Wheelers |
48 – 72 V |
1.2 – 3.3 |
|
E – Three Wheelers |
48 – 60 V |
3.6 – 8 |
|
E – Cars ( 1st
generation ) |
72 V |
21 |
|
E – Cars ( 2nd
generation |
30 – 80 V |
30 – 80 |
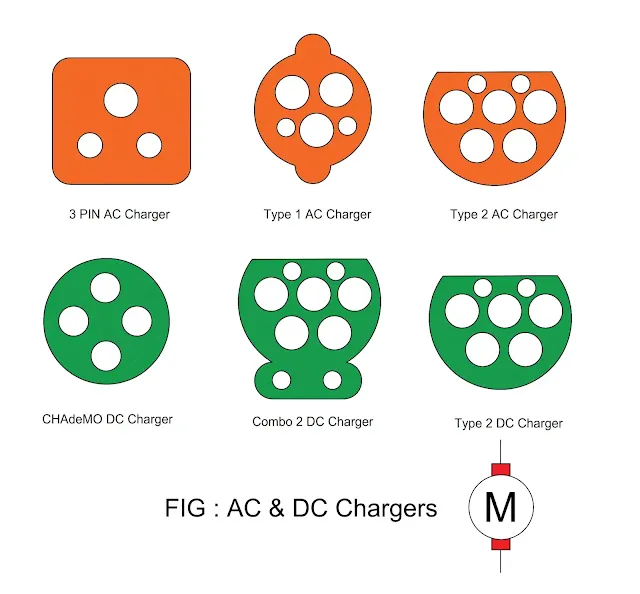
Types of EV Charger
- There are two types of chargers : AC Charger and DC Chargers
- The capacity of the AC chargers from 2 kW to 22 kW and that of DC charger is from 2 kW to 200 kW + DC.
|
Types of AC Chargers |
Types of DC Chargers |
|
3 Pin |
CHAdeMo |
|
Type 1 |
Combo 2 |
|
Type 2 |
Type 2 |
|
Modes 1 to 3 |
Mode 4 |
Methods of Charging
- The supply to battery pack is done by direct current.
- The AC supply is first converted in to DC in order to supply to battery.
- In the case of AC Electrical vehicle supply equipment ( EVSE ), the AC power is given to the on-board charger of the Electrical Vehicle which converts it to DC.
- Similarly, DC Electrical vehicle supply equipment ( EVSE ) supply DC Power directly to the battery, bypassing onboard charger.
Mode 1 Charging
- It is also known as dumb charging.
- It also permits no communication between Electrical vehicle and Electrical vehicle supply equipment
Mode 2 Charging
- The mode 2 charging is used for home charging and it has inbuilt protection and control capability.
Mode 3 & 4 Charging
- These types of chargers provide separate charger device to supply power to electrical vehicles.
- It has improved control systems and it is used for commercial / public charging.
|
charging |
Power level |
Current Type |
Types of EV |
|
Normal power |
≤ 7 kW, 7 kW ≤ P ≤ 22 kW |
AC & DC |
2 Wheels, 3 Wheels, 4 Wheels ( upto 1 tons ) |
|
High power |
22 kW ≤ P ≤ 50 kW 50 kW ≤ P ≤ 200 kW |
DC |
LCVs and MCVs ( 1 tons to 6 tons |
You may also like to read these articles
What is inductor and inductance?
Advantages of Hydrogen Cooling of Alternator









No comments:
Post a Comment