The classification of permanent magnet synchronous motor is done based
on induced emf in the it.
Brushless AC Motor
- When the waveform
of induced emf is sinusoidal, it is called as brushless AC Motor
Brushless DC Motor
- When the waveform
of induced emf is trapezoidal, it is called as brushless DC Motor.
Construction of BLDC motor
- The
configuration of BLDC motor is done on the basis of supply whether it is single
phase, two phase or three phase BLDC motor.
- Actually, the three phase BLDC
motor is used in the industries. The main parts of the BLDC motor are as below.
BLDC Motor: Stator
- The
construction of stator of BLDC motor is similar to that of three phase
induction motor stator but the stator winding distribution is different to that
of three phase induction motor.
- The stator winding is star connected and each
winding is connected through interconnection. According to interconnection of
the stator winding, the configuration of BLDC motor is
Sinusoidal BLDC Motor
- The
stator waveform of the sinusoidal BLDC motor is sinusoidal type.
- The torque
produced in the sinusoidal BLDC motor is smoother than that of trapezoidal BLDC
Motor but due to interconnection of stator winding its copper weight and cost
increases.
Trapezoidal BLDC Motor
- The
stator waveform of the trapezoidal BLDC motor is trapezoidal type.
- The voltage
waveform diagram of the three phase BLDC motor is shown in the Figure.
BLDC Motor: Rotor
- The
rotor of the BLDC motor is made of permanent magnet.
- The number of pair of
poles in the range of 2 to 8. The ferrite material is used to make permanent
magnet.
- The rotor material is selected based on necessary magnetic field
density in the rotor.
- The cost of ferrite material is less by considering
volume of rotor material but at the same time flux density in the rotor is also
less.
- The flux density of the ‘ rare
earth alloy ’ is higher than that of ferrite material for same volume of
material therefore for the same torque, the size of rotor resulting stator size
reduces when using rare earth ferrite material.
- The neodymium ( Nd ), samarium
cobalt ( Smco ), alloy of neodymium and Neodymium magnet ( NdFeB ) is used as
rare earth ferrite magnet material.

BLDC Motor: Hall sensor
- The
commutation process in the BLDC motor is done by electronic circuit.
- The stator
winding is energized in proper sequence in order to rotate BLDC Motor rotor.
- There
are three sensors placed at the non – driving end of the stator as show in the
figure.
- The function of the hall sensor is to check the position of rotor.
- The
hall sensors are placed at 120 degree to each other and commutation process is
done by them.
- When north or south pole of rotor passes closely to hall sensor,
the hall sensor generates low or high signal.
- This signal indicates north or
south pole of rotor passes through hall sensor.
- The power requires for hall
sensor may be provided form 4 Volt or 24 Volts.
- In order to make DC motor, brushless it is
considered as ‘inside out’.
- It means that the winding is placed on the stator
and rotor is made of permanent magnet.
- The reversal of current in the DC motor
is done by commutator and brushes whereas it is done by electronic switch in
the BLDC motor.
- When the response of hall sensor is low, electronic amplifier
or drive circuit works as commutator in the servo system.

Working of BLDC Motor
- The
DC supply to the BLDC motor is not given directly but it is given by reversing
through semiconductor switch for fixed rotor position.
- The torque in the BLDC
motor is produced when the stator magnetic field and magnetic field produced by
permanent magnet interact.
- The maximum torque is produced when two magnetic
fields are at 90 degrees to each other.
- The rotor moves and catch with stator
magnetic field to continuous rotation of rotor.
Torque – Speed Characteristics
- Figure
shows torque – speed characteristics of BLDC Motor.
- The BLDC can be loaded up
to rated torque during continuous operation. The torque remain constant upto
rated speed.
- When the BLDC motor run at 150% speed of rated speed, the torque
starts drooping.
- The BLDC motor is useful where frequent starts and stops and
frequent reversal of rotation with load is necessary.
Comparison between
conventional DC Motor and BLDC Motor
Commutation Sequence
- For
each commutation sequence, positive supply is given to one winding, negative
supply given to another winding and third winding is kept at de-energized
position.
- The rotor position is sensed through hall sensors placed on the
stator.
- The hall sensor changes its state ( low or high ) according to rotor
position. One hall sensor changes its state for every 60 degree of rotation of
rotor.
- It takes 6 steps to complete on electrical cycle. However, one
electrical cycle may not be equal to one mechanical revolution of rotor.
- One
electrical cycle is completed for each rotor pole pairs therefore the number of
electrical cycle is equal to number of pair of poles.
Relation between
electrical rotation and mechanical rotation
θe = (
P / 2 ) ( θm )
Where
θe =
Electrical rotation
P = Number of
poles
θm =
Mechanical rotation
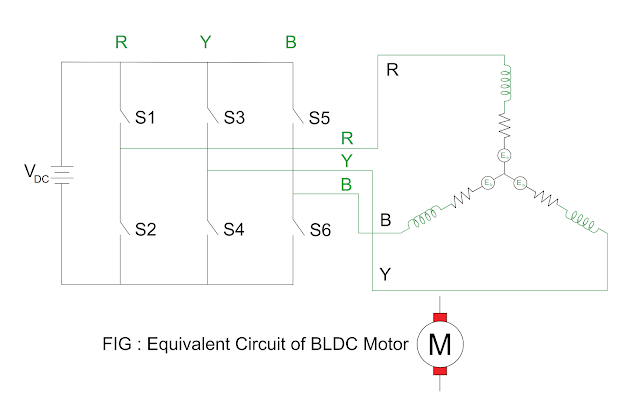
Equivalent Circuit
of BLDC Motor
- The
equivalent circuit of the BLDC motor is shown in the figure.
- The three-phase
supply to the stator winding is given through inverter.
- There are six
semiconductor switches in the three-phase inverter circuit, the switching of
semiconductor depends upon signal of hall sensors.
- The pulse width modulation
technique is used in order to switching semiconductor device.
- The frequency of
PWM is at least 10 times to that of maximum frequency of motor.
- The BJT,
MOSFET, IGBT or GTO is used as semiconductor switching device.
Switching Sequence in the BLDC Motor
- The
switching sequence for the position of hall sensor is show in the table.
- Hall
sensor – 1 shows high position whereas hall sensor – 0 shows low position.
- Figure shows position of hall sensors and current passes through coil R, coil Y
and coil B with reference to hall sensors position.
- The commutation sequence of semiconductor for six
position of hall sensor is shown in the figure.
|
Sr. No
|
Hall Sensors
|
Phase
|
Semiconductor
Switches “Switched ON”
|
|
1
|
101
|
R ( + ) – Y ( -
)
|
S1 & S4
|
|
2
|
100
|
R ( + ) – B ( -
)
|
S1 & S6
|
|
3
|
110
|
Y ( + ) – B ( -
)
|
S3 & S6
|
|
4
|
010
|
R ( - ) – Y ( +
)
|
S2 & S3
|
|
5
|
011
|
R ( - ) – B ( +
)
|
S2 & S5
|
|
6
|
001
|
Y ( - ) – B ( +
)
|
S4 & S5
|
( 1 ) The position of hall sensor H1H2H3 – 101 or electrical 60 degree, phase R gets positive supply, phase Y gets negative supply and phase B is kept in deenergized condition. This will result in semiconductor switch S1 and S4 is switched on.
( 2 ) Similarly, the position of hall sensor H1H2H3 – 100 or electrical 120 degree, phase R gets positive supply, phase B gets negative supply and phase Y is kept in deenergized condition. This will result in semiconductor switch S1 and S6 is switched on.
Applications
& Features of BLDC Motor
Applications
- Constant load: Fan,
blower, pump
- Variable load: Compressor,
dryer, washers, fuel control, electronic steering control, engine control,
robotic arm control, gyroscope control etc.
- Position control: Computer
numeric control ( CNC ) machine, process control, conveyor control
Features
- High efficiency
- High power factor
- Silent operation
- Compact
- Reliability
- Low maintenance